Equine Preventative Medicine Checklist
Along with spring comes vaccinations and preventative care appointments for our equine friends. We all understand the importance of preventative medicine, but it’s easy to miss things, so we’ve prepared a list of what you should be doing with your horse to make sure they’re healthy and prepared for summer riding season.
Vaccinations
We will start with the easiest – vaccinations. Vaccine protocol for the spring varies depending on your geography and your individual horse’s exposure potential and travel schedule. Always consult with your veterinarian if you are going to travel somewhere new with your horse. Here on the Front Range, we typically recommend a 5 way (eastern and western equine encephalitis, tetanus, rhinopneumonitis, and influenza) and a West Nile booster as the basic starting place for spring vaccinations. For a more in depth discussion of the vaccinations we recommended in Colorado and why, see the blog titled Why are the Vaccines we give in Spring So Important Here in Colorado?
Deworming
Deworming used to be easy – give your horse a deworming paste at set intervals and you’re done. But research has shown that deworming is certainly not as straightforward as we once thought it was. There are several options and differing approaches to deworming, and whether you opt to use a classical “rotational” deworming, or a more targeted “Fecal Egg count” approach, spring is a time to think about how to protect your horse from internal parasites. There are pros and cons to different deworming approaches, and we have complete articles on both of these regimes listed below.
Rotational Deworming – What’s the Right Choice?
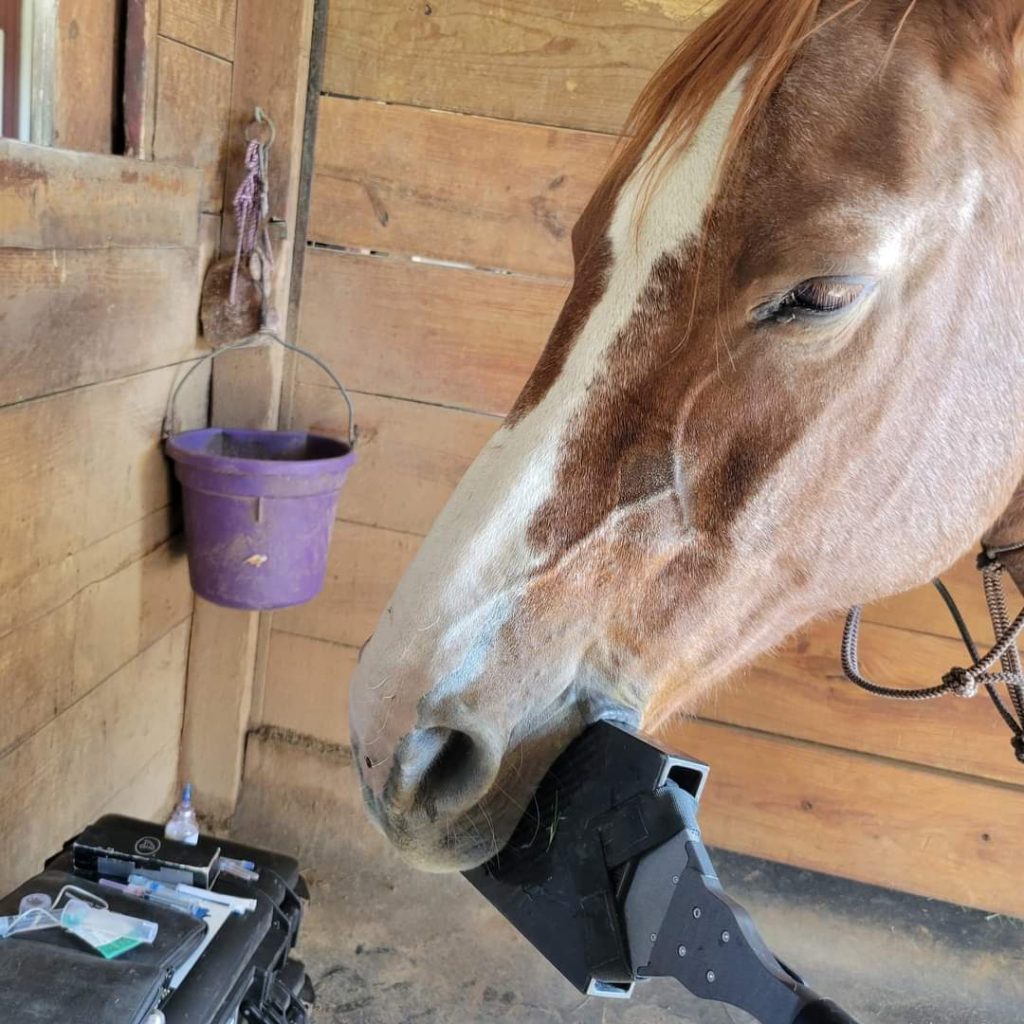
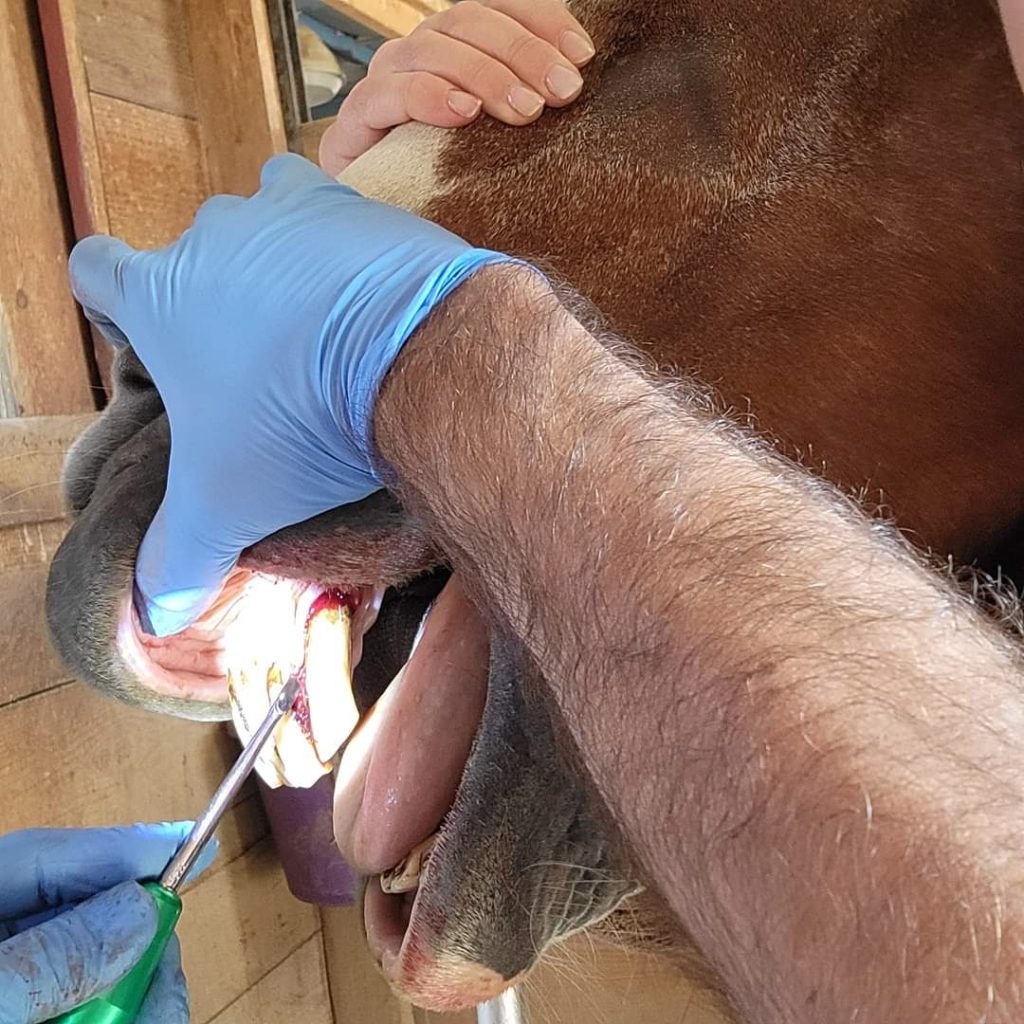
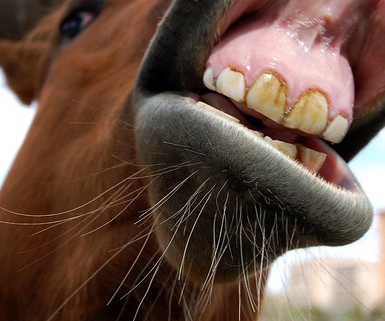
Dentistry
Although there is nothing tying teeth floating to vaccination, deworming or seasonality, most people (veterinarians included) like the convenience of combining all of the preventative medicine into a single visit. Spring is a critical time to have your horses’ teeth checked comprehensively. Tooth and other mouth issues can have a dramatic impact on your horses’ comfort, performance, and even lameness issues. Dental issues and questions like “Does my horse need a float?” are immense subjects and are covered in detail in previous issues of the blog.
Why is Regular Dentistry so Critical to your Horses’ Health?
How Do I know My Horse Needs a Float?
Why Do I Need to Float my Horses’ Teeth?
Physical Examination
A good general physical exam is a good idea for all horses this time of year so that we (both owner and veterinarian) are assured that there is no need for an alteration to the diet or that some insidious disease process is slowly creeping in unnoticed. It’s also very helpful to have a baseline of your horses’ health so when changes happen they can be noticed, and dealt with, quickly. Summer is riding and show season, and a physical examination will ensure your horse is at the top of their game, making your time together enjoyable for you both. An important aspect of the physical exam that often gets ignored is a very brief (just a few minutes) lameness exam. Whether you have noticed that your horse is tripping a bit more, or he just hasn’t been evaluated, a check of his legs could be invaluable in finding a mild issue before it is a major one. If this is something you are interested in, be sure to let the office know when you schedule your appointment that you would like the veterinarian to spend a bit of time with a lameness evaluation, so that a scheduling issue doesn’t arise.
Spring Preventative Medicine Checklist
Below is a quick reference for when your vet arrives for spring tune ups for the horses. I have had clients use this little outline as a basis for questions they have for the vet when he or she arrives. We all fall victim to “I forgot to ask while you were here” questions! Happy trails and enjoy the beautiful Colorado spring!!
Quick Checklist for Spring:
- vaccines – 5-way and West Nile Booster
- deworming or FEC – which is better for your horse?
- Dental – Does your horse need a teeth float?
- General Physical including weight evaluation, diet discussion, old age changes (ie cushings), and lameness evaluation